The 4c of Diamonds
The four basic parameters
Le 4c, diamond evaluation criteria: to ensure a correct diamond certification, there are international rules, which allow an objective evaluation in every part of the world. Between the 1940s and 1950s, the G.I.A. (Gemological Institute of America) developed the International diamond grading system. Thus giving rise to the evaluation system universally known as “4c”, as an acronym for the initials of the four fundamental parameters for the evaluation of a diamond: cut-the color cut-the colour clarity-the purity carat-the weight
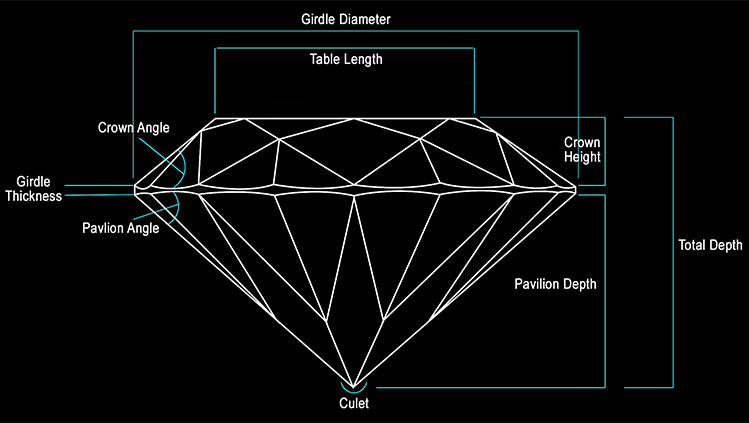
In detail: Cut-the cut: Between all the evaluation parameters, the proportion of the cutting (cutting) is by far the most important. When the proportions are perfect, all the light received from the stone is reflected from the table or from the veneers of the crown, in fact the intent is to evaluate the refractive capacity and the term cut refers not to the shape of the diamond, but to the quality of the cut. If the pavilion is too high, or otherwise shallow, the light passes through the veneers of the pavilion itself and is lost without making the stone shine.
Evaluation of the cut: the only stones classifiable as cut stones are those of 0.25 carats up the fundamental elements for the evaluation of the cutting of a diamond are:-table diameter percentage: The proportion of the width of the table relative to the diameter of the shape of the brilliant cut. -Crown height Percentage: The proportion of the crown height relative to the diameter of the shape of the brilliant cut. -Pavillon Depth Percentage: The proportion of the depth of the pavilion with respect to the diameter of the shape of the brilliant cut.
Color-the colour: If it is true that the perfect stone is colorless, it is also true that there are in nature colored diamonds often appreciated more than the white ones thanks to this characteristic, where the color is so intense as to become a merit. The color of diamonds is evaluated by illuminating the stone from the north and on the white Paper, all this to avoid the distortion by the sources of artificial natural light. The coloration is a phenomenon due to the presence (in small percentages) of chemicals that give the stone pleasing yellow, blue, green and pink tones. The only valid method to determine the exact color of the diamond is to compare it with another one that has been classified as a touchstone.
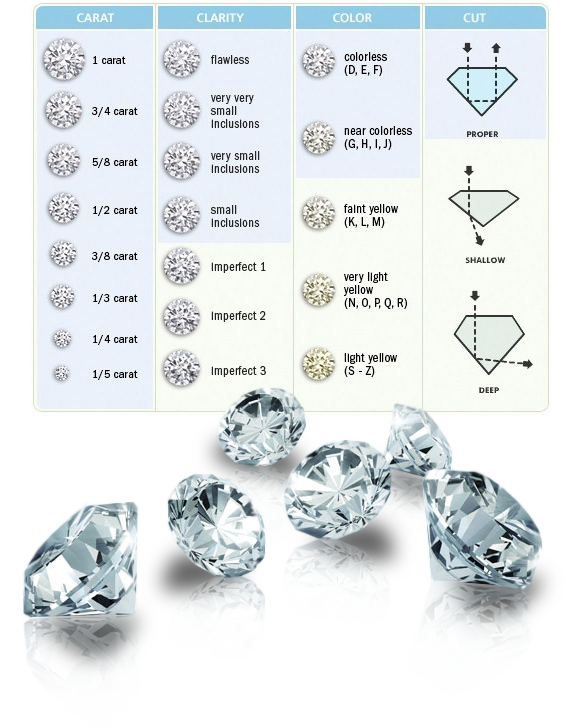
Clarity-Purity: A diamond was formed in the span of 900,000 years. In such a long period of time inside the crystal have incorporated internal microinclusions and external stains whose classification contributes to determine the value of the bud. It is therefore valued how many imperfections contains the stone and its total characteristics: external and internal.
Carat-Weight: The weight of precious stones is determined in carats. A carat corresponds to 0.20 grams; It takes five stones of 1 Ct. To match the weight of 1 gram. The carat, in turn, is divided into 100 parts: 1 cent of Carat equals 1 point. It seems that the adoption of the Carat, as a unit of measurement, it dates back to 1200 and is due to Marco Polo, who, in the need to uniforme, in the various markets with which he met, a unit of equal weight for all, used the seeds of the carob (carat in Arabic). The seeds of the carob have the characteristic of having always the same weight, whether it be the gigantic carob of the savannah and of the tiny fruits of the areas with temperate climate. Now you use different methods of course, using electronic microbalances that can measure the weight up to five digits after the comma. Monitoring the weight throughout the process of machining a diamond is definitely a fundamental security operation.